- July 10, 2020
- Posted by: Interwest Communications Team
- Categories: News, Uncategorized

Access control systems go beyond just having a lock on a door. These systems are part of an ecosystem that’s designed to control and restrict access to a business’ data, property, and assets. These systems are designed to provide holistic protection of property, sensitive information, and protection from damage.
As the installation and support professionals for phones, data, and security, we at Interwest Communications know access control systems can be confusing. In this article, we’ll take a look at the different ways in which access control can provide protection of a given property, as well as outlining the most common protocols for access control systems.
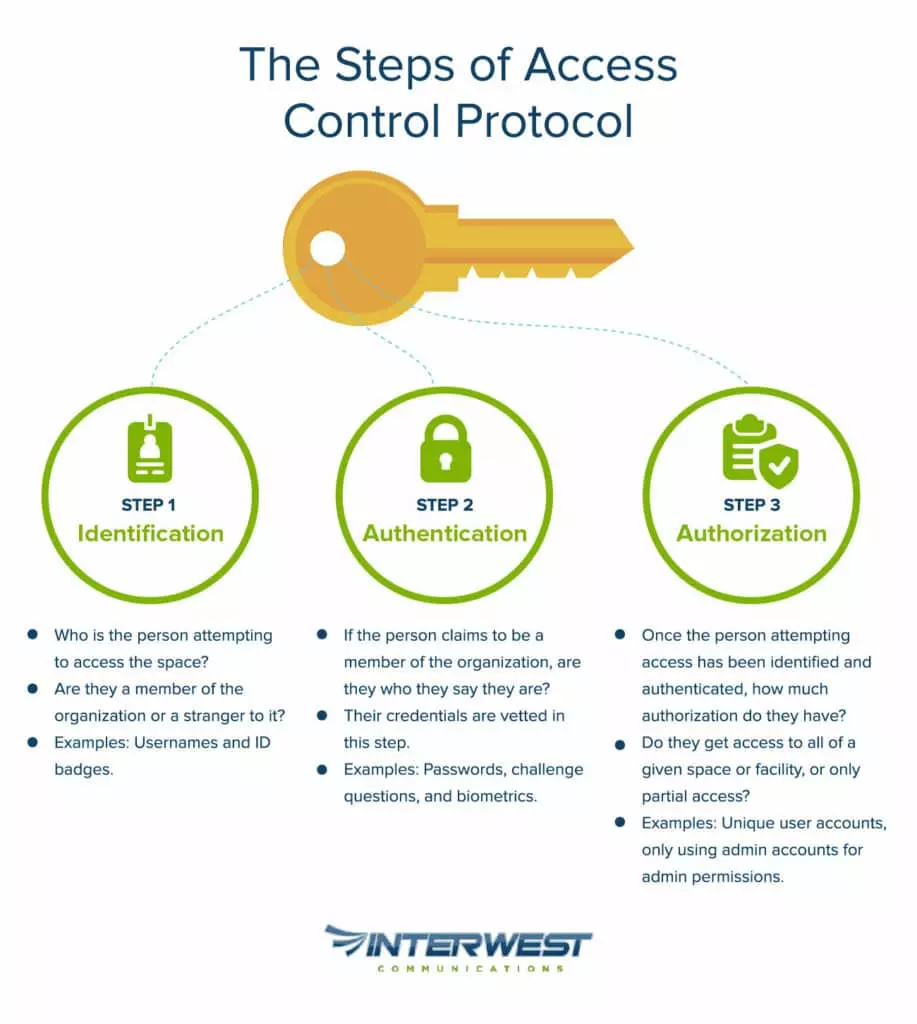
Walking Through the Steps of Access Control Protocols
Broadly speaking, access control breaks down into 3 steps.
1. Identification – Who is the person attempting to access the space? Are they a member of the organization or a stranger to it?
2. Authentication – If the person claims to be a member of the organization, are they who they say they are? Their credentials must be vetted in this step.
3. Authorization – Once the person attempting access has been identified and authenticated, how much authorization do they receive? Do they get access to all of a given space or facility, or only partial access?
Types of Access Control
Access control is divided into categories based on both implementation and function. Many different access control methods fall under both categories, but we’ll define both here for clarity.
Types of Access Control Systems
Types of access control systems can be categorized based on the platform that they operate on. There are 4 main types of access control systems:
1. On-Premise Access Control Systems
2. Web-Based Access Control Systems
3. Mobile-Based Access Control Systems
4. Internet of Things (IoT-Based) Access Control Systems
1. On-Premise Access Control Systems
Also known as locally hosted access control, on-premise systems are installed on servers and devices that are managed on site. These systems can only be physically accessed on the premise. The benefit of this system is the level of customization and control an organization has over the system, but it is limited by their IT capabilities.
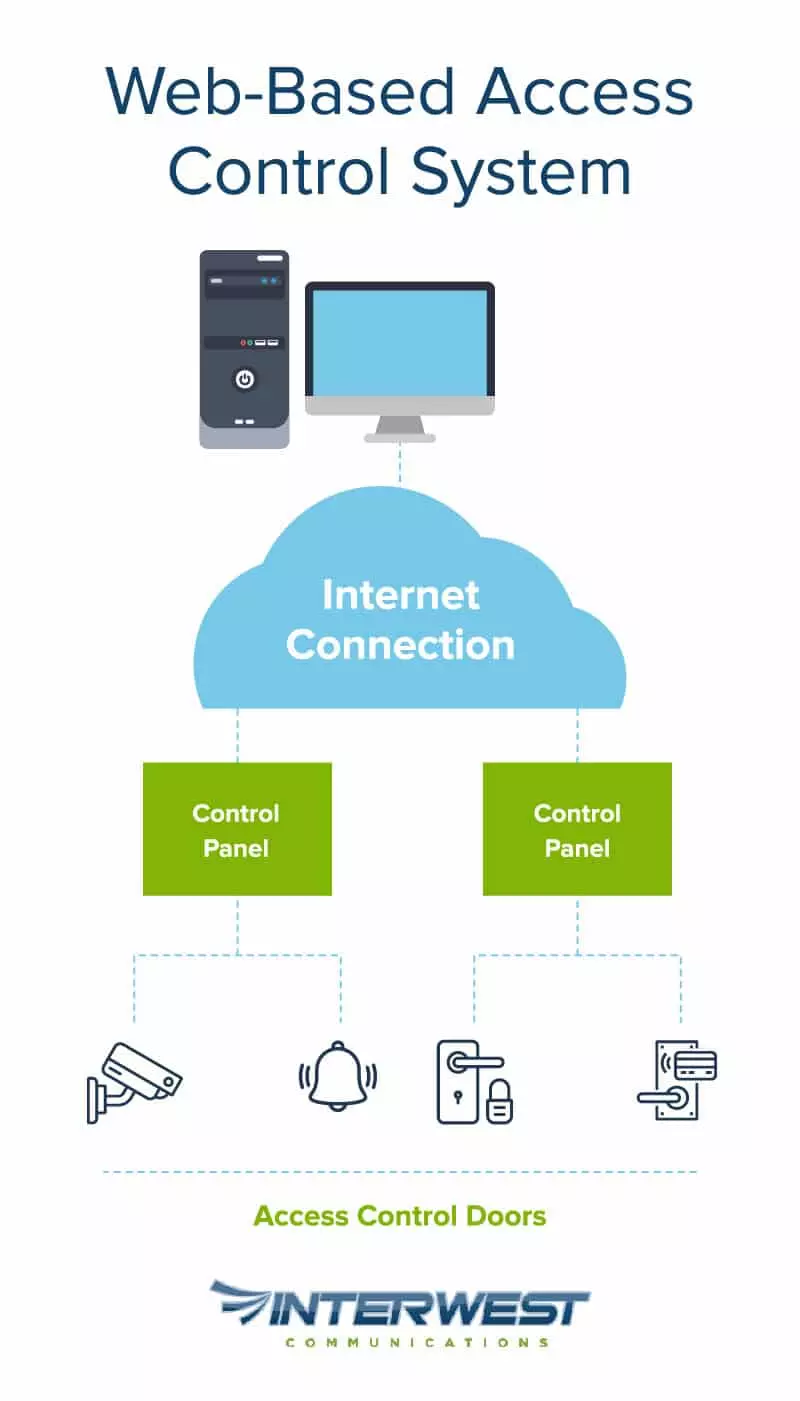
2. Web-Based Access Control Systems
Also known as cloud-based access control, web-based systems store user permissions on the web, rather than in physical devices, enabling administrators to view, manage, and control permissions from anywhere. These systems also automate updates and have options for vacations and other conveniences. They’re low cost, and can be deployed easily.
3. Mobile-Based Access Control Systems
Access control systems that are mobile base can be managed through a smartphone, which sends an unlock code to a cloud server via wi-fi or cell signal. Using a smartphone system allows you to unlock entry points into a business from anywhere, which can be useful for granting one-time access. There are also devices that use Bluetooth or near-field communication (NFC) to unlock doors, which can be a great benefit to your security systems.
4. IoT-Based (Internet of Things) Access Control Systems
Most access control systems are now connected to the internet and utilize firmware to keep things updated in real-time. This is part of systems called the Internet of Things. The wide distribution of security protocols between many different systems will help prevent unauthorized devices from communicating on the network.
Types of Access Control Management
Access control management are the protocols used to determine and control user access. There are 4 types of access control management:
1. Mandatory Access Control(MAC)
2. Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
3. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
4. Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
1. Mandatory (MAC)
This is the strictest option and is primarily used by the military and other government entities. The operating system firmly controls access to all doors based on settings created by the system administrator. With a MAC system, it’s impossible for users to change permits that grant or deny entry to rooms throughout the facility.
2. Discretionary (DAC)
This is the default option for managing most access control systems. Unlike MAC, DAC allows business owners to make decisions about who can access which areas on the premises. Each entry point has an Access Control List (ACL) with groups or individual users who have permission to enter.
3. Role-based (RBAC)
Also called non-discretionary access control, this form of access control grants entry to users based on their role within the organization. As with DAC, this management style ties access to ACLs. RBAC makes rules that grant access only at certain times of the day or days of the week.
4. Attribute-based (ABAC)
ABAC manages access rights by evaluating a set of rules, policies, and relationships using the attributes of users, systems, and environmental conditions.
Types of Access Control Based on Implementation
An effective access control system combines administrative, physical and technical access control to limit access to sensitive data, networks, and physical locations.
1. Administrative – An important aspect of access control implementation is administrative, often existing outside of the individual piece of technology that controls access. Policies and procedures are a part of this.
2. Physical – Physical access control are barriers that prevent physical access of an area. Fences, gates, and doors are examples of physical implementations of access control. The use of locks, badges, biometrics (facial recognition, fingerprints), turnstiles, video surveillance cameras, security guards, motion detectors, and the like controls access.
3. Technical – Technical limitations limit access to computer networks, system files, and other sensitive data. These include firewalls, antivirus software, and multi factor authentication (or 2FA).
Types of Access Control Based on Function
Access control can also be classified based on how they function.
1. Preventative – Preventive functions are deployed to stop the unauthorized activity from occurring in the first place. Examples of preventative access control include:
-
Fences
-
Locks
-
Biometrics
-
Lighting
-
Alarms
-
The separation of duties
-
Job rotation
-
Data classification
-
Penetration testing
-
Encryption
-
Auditing
-
Security cameras or closed-circuit television (CCTV)
-
Smart cards
-
Security policies
-
Antivirus software
2. Deterrent – Deterrents are deployed to discourage the violation of security policies. Deterrents are functions that go beyond prevention and try to create consequences for violating the access control system. Examples include:
-
Security guard
-
Mantraps
-
Fences
-
Alarms
-
Encryption
-
Auditing
-
Firewalls
3. Detective – Detective functions are usually deployed to discover unwanted or unauthorized activity. Detective access control includes:
-
Security guards
-
Guard dogs
-
Motion detectors
-
CCTV
-
Supervision and review policies
-
Incident investigations
4. Corrective – Corrective functions are used to restore a system to normal after unauthorized activity. Examples of corrective access control include:
-
Antivirus solutions
-
Alarms
-
Security policies
5. Compensation – Compensation functions are deployed to give options and support to other controls in support of a security policy. They’re often more desirable to damaging controls. Examples of compensation access control include:
-
Personnel supervision
-
Monitoring
-
Work task procedures
6. Directive – Directive functions are designed to confine and control the actions of a subject to encourage compliance with security policies. Examples of this include:
-
Posted notifications
-
Monitoring
-
Supervision
-
Security guards
Benefits of Access Control Systems
Access control is just one layer of security, but it touches on many aspects that can benefit other areas of the organization.
Benefit 1. Knowing Who is Coming & Going
Most businesses have valuable equipment and physical assets that need to be tracked to make sure that they aren’t lost. If a business is large with a lot of employees, it can be difficult for everyone to know who is an employee and who is not. Access control helps prevent strangers from slipping in undetected.
Benefit 2. Keep Track of Employees
Access control can help businesses track employees across multiple shifts and who are working at odd hours, forming an essential part of organizing the chaos of a thriving business.
Benefit 3. Secure Data & Sensitive Information
Most businesses have sensitive data and information about business operations or their clients. Making sure that access is limited to certain areas is essential.
Benefit 4. Reduce Accidents & Theft
With proper access control methods in place, accidents around sensitive or dangerous equipment are greatly reduced, along with theft reduction.
Benefit 5. Multi-Property Protection
If you have a business with multiple locations, an integrated access control system will allow a business to grant access to employees who need to enter multiple or all buildings.
Benefit 6. Never Worry about Keys
Keys pose a serious security risk because they can be duplicated and need to be tracked. With a system that is not key-based, the chance of a disgruntled or former employee causing damage to your business is reduced.
The Best Access Control Systems Provider
For over 30 years, Interwest Communications has been serving businesses of all sizes by providing NEC business telephone systems, structured cabling infrastructure, unified messaging solutions, data networking services and technologies, local phone service, and security. You can start creating a more holistic security solution, including access control systems, today by booking a free consultation.
